Optimize your cardiovascular risk assessment with our CHADS Calculator. Simplify the evaluation of stroke risk in atrial fibrillation patients, ensuring informed decisions for effective treatment strategies.
RESULTS
Deciding on the best care for patients with heart rhythm issues can be challenging. A tool like the CHADS score calculator plays a vital role in this process. This guide will help you understand and utilize the CHADS score to enhance patient treatment strategies effectively.
What is the CHADS SCORE CALCULATOR?
The CHADS SCORE CALCULATOR is a clinical tool designed to estimate the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. It guides physicians in decisions regarding antithrombotic therapy by providing an easy-to-use, evidence-based scoring system.
Purpose
Doctors use the CHADS SCORE CALCULATOR to figure out stroke risk in people with atrial fibrillation. This tool helps decide if someone needs antithrombotic therapy, like warfarin or aspirin, to prevent strokes.
It gives doctors a clear method to spot patients who have a higher chance of having a stroke. With this calculator, they can choose the best treatment for patients more effectively.
The tool turns complex medical data into simple scores that guide patient care decisions.
It’s also key for managing atrial fibrillation treatments and improving how well these treatments work. By using the CHADS SCORE CALCULATOR, healthcare providers can give safer and better care to their patients.
They make sure only those who need it get strong medicine to prevent blood clots and strokes.
Features
The CHADS SCORE CALCULATOR stands out for its ease of use and speed. Healthcare providers can quickly enter patient information like heart failure history and age to get a stroke risk score.
This tool has made it easier to decide on the best treatment for atrial fibrillation patients. With just a few clicks, doctors receive clear guidance on whether to recommend blood thinners.
This calculator also supports evidence-based medicine by using medical data from studies. It’s designed with patient safety in mind, helping prevent strokes in those with cardiovascular issues.
By considering factors like hypertension and diabetes, the tool ensures each person gets personalized care based on their specific health profile. Also, try our CHADS VASC Calculator, a comprehensive tool to assess stroke risk in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Components of the CHADS Score
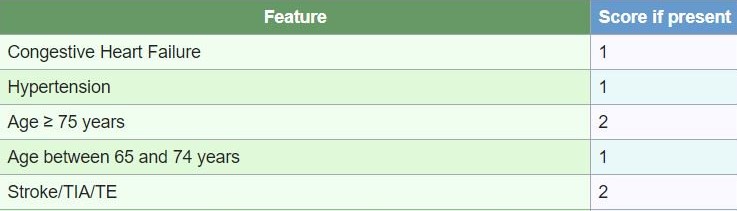
Congestive heart failure scores one point on the CHADS calculator. If you have high blood pressure, that’s another point. Being 75 or older adds yet another. Diabetes counts for one more point too.
Lastly, if you’ve had a stroke or TIA, it also contributes to your score.
Each factor increases your risk of having a stroke related to atrial fibrillation. Doctors use this system to decide on the best treatment plan for preventing future strokes. Next, let’s explore why this score matters so much in cardiology and how it helps patients and doctors alike.
Congestive Heart Failure
Moving from the general components of the CHADS score, let’s focus on heart health. Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a key element in determining stroke risk for patients with an irregular heartbeat known as atrial fibrillation.
Doctors use this condition to help calculate how likely a patient is to have a stroke. If someone has congestive heart failure, they get one point added to their CHADS score.
Having CHF means the heart can’t pump blood well enough throughout the body. This problem increases the chance of blood clots forming in the heart, which could travel to the brain and cause a stroke.
So doctors need to consider CHF when they look at stroke risks in their patients with atrial fibrillation. This helps them decide if blood thinners are needed for protection against strokes. Also, try our BMI BSA Calculator, a quick way to determine your body mass index and surface area for a holistic health assessment.
Hypertension History
After considering congestive heart failure, the CHADS score calculator also looks at hypertension history. This part is crucial because high blood pressure can harm blood vessels and make clots more likely.
Doctors give 1 point for a history of hypertension in the CHADS score calculation.
Having high blood pressure increases stroke risk for people with atrial fibrillation. The calculator uses this information to help doctors decide on treatments like oral anticoagulation therapy.
It’s simple: if a patient has ever had hypertension, they get an extra point in their assessment. This helps ensure that patients receive the right care to prevent strokes.
Age 75 and older
People who are 75 or older have a higher risk of stroke. The CHADS score calculator counts this age as a major factor. This group gets an extra point because their stroke risk is greater.
So in the CHADS score, being over 75 adds two points to the total score.
Doctors pay close attention to patients’ ages when they use the CHADS score. Older people often need more care to prevent strokes. Knowing someone’s age helps doctors decide if they need medicine to stop blood clots.
Diabetes History
Moving on from age, diabetes history is another critical component of the CHADS score. If a patient has diabetes mellitus, they get an additional point in their assessment. This reflects the increased risk of stroke that diabetes brings to those with atrial fibrillation.
Managing blood sugar levels becomes crucial for these patients. It’s not just about controlling diabetes—this also helps lower their overall stroke risk.
Having a history of diabetes means doctors will watch these patients more closely if they have atrial fibrillation. They might need extra care or different treatments to prevent blood clots from forming.
The CHADS score calculator uses this information to help guide treatment options like oral anticoagulants, ensuring safety and effectiveness for each individual’s needs. Also, try our BISAP Calculator, and assess the severity of acute pancreatitis with this useful tool for healthcare professionals.
Stroke or TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack) Symptoms
After considering diabetes history in the CHADS score, another crucial factor is a patient’s past stroke or TIA symptoms. If someone has had a stroke or a TIA before, it means their brain didn’t get enough blood at some point.
This is serious because it can happen again. The CHADS score calculator counts each time you’ve had these problems. One point gets added to your total score for every past stroke or TIA event.
This part of the CHADS score is vital for making sure patients who need extra help to prevent strokes get the right treatment. A high score signals doctors that they may need to suggest stronger medicine like warfarin anticoagulation or newer oral drugs that can lower stroke risk.
It helps them be more careful with these patients and keep their heart health on track.
CHA2DS2-VASc Score Calculator Formula Explanation
The CHADS2 score is a clinical prediction rule for estimating the risk of stroke in patients with non-rheumatic atrial fibrillation (AF), a common and serious heart arrhythmia. It is used to guide decisions about anticoagulation therapy.
CHADS2 stands for:
C – Congestive heart failure (1 point) H – Hypertension (1 point) A – Age ≥75 years (1 point) D – Diabetes mellitus (1 point) S2 – Stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) (2 points)
Each of these factors is assigned a score, and the total score indicates the patient’s risk of stroke.
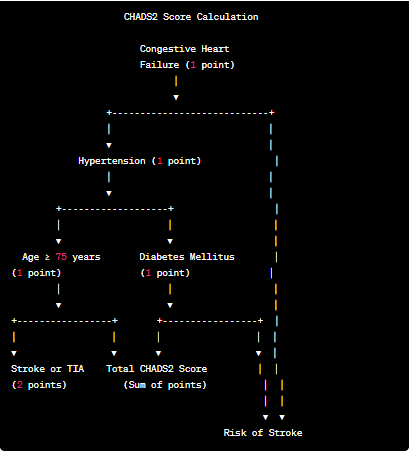
Here’s a graphical representation of the CHADS2 score calculation:
The score is calculated by assigning points to each factor and summing them up:
- Congestive heart failure: 1 point
- Hypertension: 1 point
- Age ≥75 years: 1 point
- Diabetes mellitus: 1 point
- Stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA): 2 points
The total CHADS2 score is the sum of these points, and it indicates the patient’s risk of stroke. The higher the score, the greater the risk of stroke, and consequently, the more likely anticoagulation therapy is recommended.
Why Is It Important In Cardiology?
The CHADS score calculator is a crucial tool for cardiologists as it assists in quantifying the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation, guiding treatment decisions, and enhancing patient outcomes.
This scoring system plays an integral role in the management and prevention strategies for those at elevated risk of thromboembolic events.
Identifying Stroke Risk
Identifying stroke risk is a key part of caring for patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). The CHADS2 score calculator plays a crucial role in this. It looks at several factors like heart failure, high blood pressure, age over 75, diabetes, and past strokes or TIAs.
Each factor counts as a point on the score.
A higher CHADS2 score means someone has a greater chance of having a stroke. Doctors use this number to decide how to stop strokes before they happen. They might choose blood thinners or other treatments based on the results.
Checking the CHADS2 score often helps doctors keep their patients safe from strokes.
Better Risk Stratification
Doctors need to know who has a higher chance of stroke. The CHADS score calculator helps with this. It uses clear points for each risk like heart failure or high blood pressure. A patient’s total score shows their stroke risk.
This makes doctors sure about the care needed, especially for atrial fibrillation patients.
The tool guides choices about treatments like blood thinners. It also shapes decisions for regular INR monitoring. Having a standard way to measure risk leads to better and safer care plans for patients with different health backgrounds. Also, try our QTc Calculator to evaluate your corrected QT interval to better understand your heart’s electrical activity.
How to Use the CHADS SCORE CALCULATOR?
Using the CHADS SCORE CALCULATOR is straightforward:
- Individuals or healthcare providers enter specific medical history details, and the tool quickly evaluates stroke risk in patients with atrial fibrillation.
- This calculation aids in informed decision-making regarding anticoagulation therapy to prevent ischemic strokes effectively.
- Input Information (CHF history, Hypertension history, Age ≥ 75 years)
- To use the CHADS score calculator correctly, you must know if there’s a history of congestive heart failure (CHF). Knowing about any hypertension history is also key. Make sure to note if the person is 75 years old or older.
- This age factor is especially important because it adds more points to the risk assessment. You will need this information for an accurate stroke risk analysis.
- Next, include any diabetes and prior strokes or TIA symptoms in your input data. These details help pinpoint how likely a stroke could happen.
Diabetes History and Stroke or TIA Symptoms
If you have diabetes, your chance of a stroke goes up. This is because high blood sugar can harm your blood vessels over time, making clots more likely to form. These clots can block blood flow in the brain leading to a stroke.
Having diabetes puts it on your CHADS score.
Past strokes or TIA symptoms tell doctors you could be at risk for another stroke. A TIA is like a mini-stroke where blood flow is briefly blocked. Both conditions add points to your CHADS score because they signal that something might already be wrong with the blood flow in your brain.
Results
The CHADS SCORE CALCULATOR gives a number to show stroke risk in patients with atrial fibrillation. High scores point out a greater risk and suggest that anticoagulant therapy could help prevent strokes.
Doctors use this score to decide if blood-thinning medicine is right for the patient. They look at each part of the score: heart failure, high blood pressure, age, diabetes, and past strokes or TIAs.
This tool makes it easier for doctors to treat and manage atrial fibrillation properly.
By understanding a patient’s score, healthcare professionals improve care quality. They can choose better treatments that lower stroke chances in these patients. The calculator helps ensure that each person gets the most fitting treatment based on their unique risks from atrial fibrillation. Also, try our Creatinine Calculator, assess your creatinine levels, and gain insights into kidney function.
Related Calculators and Tools
Patients with atrial fibrillation can find out their stroke risk using the CHA2DS2-VASc score calculator. It includes factors like vascular disease and age. For those on blood thinners, the HAS-BLED score predicts bleeding chances.
The ATRIA tool also judges bleeding risks during atrial fibrillation treatment.
Other calculators like ABC and R2CHADS2 offer stroke risk assessments for such patients. Doctors use HEMORR2HAGES to see how likely a patient is to have bleeding issues when they have atrial fibrillation.
These tools support healthcare choices and match patients with the best care for preventing strokes or managing bleeding while on medication.
FAQs
1. What is a CHADS score calculator?
A CHADS score calculator is a tool that doctors use to find out your risk of having a stroke if you have atrial fibrillation. It looks at different stroke risk factors and helps decide if you need medicine to prevent clots.
2. Why do doctors use the CHADS score?
Doctors use the CHADS score to help them make smart choices about preventing strokes in people with atrial fibrillation. By knowing someone’s risk level, they can pick the best treatment like blood thinners or novel oral anticoagulants.
3. What do doctors consider when calculating my CHADS score?
When calculating your CHADS score, doctors think about things like how old you are, whether you’ve had heart problems or a stroke before, and other health issues like diabetes or high blood pressure that could cause serious bleeding issues.
4. Can patients share their thoughts on using the CHADs calculator for treatment?
Yes! Patients can talk with their doctors about what they want and any worries they might have regarding treatments suggested by using the scores from this risk assessment tool during clinical practice.
5. Do medical residents also learn how to use the CHADS Score Calculator?
Medical residents learn how to use the CHADS Score Calculator as part of their training in managing diseases like atrial fibrillation following guidelines recommended by experts in cardiovascular medicine.
Related Calculators: