Assess your liver health effortlessly with our user-friendly calculator! Whether you’re a healthcare professional or simply interested in your liver’s well-being, this tool is here to assist you.
RESULTS
When faced with liver cirrhosis, understanding the severity and prognosis is a crucial concern. The Child-Pugh calculator emerges as a key tool in this context – it predicts mortality risks for those battling this condition.
This guide will tell you how our intuitive Child-Pugh Calculator provides vital information to patients and health professionals alike, aiding critical healthcare decisions. Discover your path to clarity—read on.
Understanding the Child-Pugh Calculator
The Child-Pugh Calculator stands as a crucial tool in the realm of hepatology, providing insight into the severity of liver cirrhosis and its associated mortality risk. This clinical instrument merges key physiological metrics to offer a comprehensive perspective on patient condition — guiding healthcare professionals through finely-tuned assessments and critical decision-making pathways for those grappling with compromised hepatic function.
Purpose and Function
A Child-Pugh calculator is a tool doctors use to see how well the liver works in someone with cirrhosis. It looks at different things like bilirubin and albumin levels, whether the person has swelling in their belly (ascites), problems with brain function (encephalopathy), and how well they eat.
By checking these, the calculator figures out a score. This score helps guess if someone might need a new liver and how soon that might be.
This score also tells doctors about how serious the liver disease is by putting patients into groups A, B, or C. Group A means the liver is doing better than those in Group C. Knowing this helps make good choices for treatments, like if it’s safe to do surgery or not.
With this info, caregivers can plan better care for people who are sick because of their liver problems.
Variables Included in the Calculation
The Child-Pugh calculator takes into account five key factors to check on liver health. These include total bilirubin and albumin levels, which tell about the liver’s ability to perform its vital tasks.
It also looks at INR – this is a test that measures how long it takes for blood to clot, pointing out issues with bleeding or bruising. Ascites refers to fluid build-up in the belly; doctors check if it’s not there, slight, or moderate.
Finally, encephalopathy is tested for any confusion or poor brain function because of liver problems.
Doctors use these factors together to score the liver’s condition from 5 to 15 points. The higher the number, the more serious the illness might be. This score helps them figure out if someone has mild (Class A), moderate (Class B), or severe (Class C) liver cirrhosis.
They can then make better choices for treating and caring for their patients’ livers. Also, try our Geriatric Depression Calculator, a tool to assess and understand depressive symptoms in older adults.
Child-Pugh Score Calculation Overview
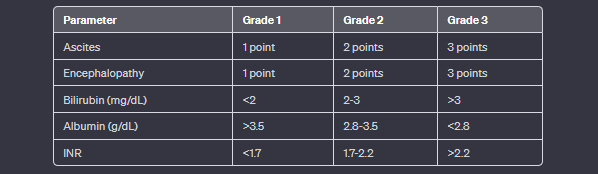
The Child-Pugh score is used to assess the severity of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. It’s based on five clinical parameters: ascites, encephalopathy, bilirubin levels, albumin levels, and prothrombin time (INR). Here’s how the scoring system works:
Ascites and Encephalopathy:
Ascites and encephalopathy are graded separately from 1 to 3, with 1 being the least severe and 3 being the most severe.
Ascites:
- Grade 1: No or mild ascites
- Grade 2: Moderate ascites
- Grade 3: Large or refractory ascites
Encephalopathy:
- Grade 1: Subtle changes in mental status
- Grade 2: Confusion or somnolence
- Grade 3: Coma
Bilirubin Levels:
- Serum bilirubin levels are measured in mg/dL.
- Less than 2 mg/dL is given 1 point, 2-3 mg/dL is given 2 points, and greater than 3 mg/dL is given 3 points.
Albumin Levels:
- Serum albumin levels are measured in g/dL.
- Greater than 3.5 g/dL is given 1 point, 2.8-3.5 g/dL is given 2 points and less than 2.8 g/dL is given 3 points.
Prothrombin Time (INR):
- INR measures the clotting tendency of blood.
- INR less than 1.7 is given 1 point, 1.7-2.2 is given 2 points, and greater than 2.2 is given 3 points.
After assigning points for each parameter, the total points are summed up to determine the Child-Pugh score, which falls into one of three categories:
- Class A: 5-6 points
- Class B: 7-9 points
- Class C: 10-15 points
This score correlates with the severity of liver disease, with Class A indicating less severe disease and Class C indicating the most severe disease.
Here’s a simplified representation of the scoring system:
Benefit Of The Calculator
- A calculator like this one can be a true lifesaver. It lets doctors quickly figure out how well your liver is working and what kind of care you might need. For someone with liver problems, it’s really important to know if they are doing okay, getting worse, or needing something like a new liver.
- This tool uses details about bilirubin, albumin levels, INR score, whether there’s fluid in the belly (ascites), and brain issues from poor liver function (encephalopathy) to give answers.
- Doctors get to see scores that tell them if the patient’s liver problem is class A, B, or C. These classes help predict chances of living for up to two years after treatment which makes planning the next steps much easier.
- They also use these scores when they think about surgeries or other big treatments – knowing the risks helps everyone make better decisions. With this calculator’s help, patients get the right treatment faster and have a clearer picture of what lies ahead for their health and life expectancy.
Also, try our Creatinine Calculator, assess your creatinine levels, and gain insights into kidney function.
Interpreting the Child-Pugh Score
Interpreting the Child-Pugh Score is a pivotal step in defining the severity of liver cirrhosis, as it correlates clinical variables with expected outcomes—this dynamic score crystallizes patient assessment and prognostication into actionable insights.
Understanding this metric paves the way for tailored medical strategies, reinforcing its essential role in managing liver disease.
Classifying Patients into Grades A, B, and C
People with liver problems get put into groups to show how severe their condition is. These groups are Grades A, B, and C. Grade A means the liver still does its job well even though it’s sick.
People in this group have a good chance of living longer, with most still alive after one year and many after two years.
Grade B is when the liver is hurting more but can still work okay. Survival for folks in this bracket drops a bit compared to Grade A. Many live past the first year and over half make it beyond two years.
Then there’s Grade C—the toughest group to be in because the liver is very ill here. This situation makes things risky, as less than half will survive one year and only some will reach two years.
Knowing which grade someone falls into helps doctors choose the right treatment. It shows whether they need new medicine or even a liver transplant to feel better.
Predicting Survival Rates and Life Expectancy
Doctors use the Child-Pugh score to guess how long a person with liver cirrhosis might live. The score can show if the liver is still doing its job well or if it is getting worse. A higher score means more serious liver problems, which can affect survival rates and life expectancy.
For example, patients in Class A tend to live longer than those in Class C. Knowing this helps doctors decide on treatments.
After figuring out the Child-Pugh score, healthcare teams have a better idea of what might happen next for someone with liver disease. They learn whether a patient faces high risks during surgery or if they should think about a liver transplant sooner rather than later. Also, try our QTc Calculator to evaluate your corrected QT interval to better understand your heart’s electrical activity.
Clinical Application of the Child-Pugh Calculator
In the hands of healthcare professionals, the Child-Pugh Calculator becomes an essential tool for evaluating liver function — providing critical insights that shape patient management strategies.
From determining surgical viability to prioritizing transplant candidacy, this calculator underpins key clinical decisions in managing liver cirrhosis complications effectively.
Assessing Liver Function and Surgery Requirements
Doctors use the Child-Pugh calculator to check how well a person’s liver works. The score tells them about the liver’s health and if someone is strong enough for surgery. For example, people with better scores can often handle operations better.
Before deciding on surgery, doctors look at things like bilirubin and prothrombin time because these numbers help predict if a patient might have problems during or after the operation.
Patients in Class A usually do fine, but those in Class C face high risks. Knowing this helps doctors and patients make smart choices about treatments like transplants or other big surgeries.
Prognosis and Need for Liver Transplant
Knowing how well the liver works helps doctors figure out if a patient needs a new one. The Child-Pugh score is very important in this. It tells us if the liver is doing okay (Grade B) or not so good (Grade C).
For people with Grade C, their liver is in bad shape, and they might need to get a transplant soon.
The survival rates tell us more about who needs a new liver too. Class A patients have better chances, but Class B’s risks are higher and Class C’s situation is much worse—many do not survive without a transplant.
This score alerts doctors—it’s like saying “Hey, it might be time for a serious talk about getting you on the list for a new liver.” Getting this right can save lives, as choosing who needs a transplant is super important. Also, try our CHADS VASC Calculator, a comprehensive tool to assess stroke risk in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Importance of the Child-Pugh Score
The Child-Pugh Score is a game-changer in hepatology, wielding significant power over clinical decision-making and outcomes for patients with cirrhosis. This tool not only steers treatment strategies but also serves as a key indicator in determining the urgency for interventions like liver transplantation – essentially shaping the journey of patient care from diagnosis to potential surgery.
Impact on Treatment Decisions
Doctors use the Child-Pugh score to make smart choices about treating liver problems. This score tells them how sick a patient’s liver is. With this information, doctors can decide if someone needs a new liver through a transplant or if they can have surgery safely.
For instance, people with a Class A score might be okay for an operation because their livers work better and they’re likely to live longer after the surgery.
Patients with worse scores, like Class C, may need careful thinking before treatment. They might not handle tough treatments well because their livers are very sick and their chance of living long is lower.
The calculator helps doctors avoid risks and pick the best care plan for each person’s health.
Role in Evaluating Suitability for Surgical Intervention
The Child-Pugh score steps in as a crucial tool when doctors have to decide if someone with liver cirrhosis can safely go through surgery. It looks closely at how well the liver is working and if it can handle the stress of an operation.
A good score may mean a green light for necessary procedures like fixing hernias or removing tumors.
But let’s say the score isn’t so great; this might suggest that surgery could be too risky. For patients hoping for a transplant, their Child-Pugh score is also key—it helps figure out who needs a new liver soonest.
This calculator does more than gauge risk—it guides surgeons and patients towards safer choices, making sure each step taken is the right one for health and recovery.
| Clinical Measure | Points |
|---|---|
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | |
| <2 | 1 |
| 2-3 | 2 |
| >3 | 3 |
| Serum Albumin (g/dL) | |
| >3.5 | 1 |
| 2.8-3.5 | 2 |
| <2.8 | 3 |
| INR | |
| <1.7 | 1 |
| 1.7-2.3 | 2 |
| >2.3 | 3 |
| Ascites | |
| None | 1 |
| Controlled with medication | 2 |
| Refractory despite treatment | 3 |
| Hepatic Encephalopathy | |
| None | 1 |
| Grade 1-2 | 2 |
| Grade 3-4 | 3 |
Feature Of Our Calculator
Our calculator makes figuring out liver health simple and quick. You plug in numbers for bilirubin, albumin, INR, ascites, and encephalopathy. Straight away, you get a score that tells you about the liver’s condition.
This helps doctors decide on treatments or if surgery is safe.
You can see if a liver transplant might be needed and how long someone with liver problems may live. The tool is easy to use – just click “Calculate” after choosing values! It also shows life expectancy and risks around belly surgery right on your screen. Also, try our BISAP Calculator, and assess the severity of acute pancreatitis with this useful tool for healthcare professionals.
Step-by-Step Guide on How Our Calculator Works
- Bilirubin value: Navigating through our Child-Pugh Calculator begins with selecting the appropriate Bilirubin value—whether it’s less than 2 mg/dL, between 2-3 mg/dL, or above 3 mg/dL.
- Albumin range: Choosing an Albumin range that best fits the patient’s condition; each choice incrementally builds toward a comprehensive assessment of liver function and potential treatment pathways.
- INR Value: INR stands for International Normalized Ratio; it tells us how fast your blood clots are compared to normal clotting time—if yours is less than 1.7, between 1.7–2.2, or over 2.2, pick that range.
- Ascites values! Ascites means extra fluid in the space between tissues lining the abdomen and abdominal organs—it could be a sign of serious liver problems like cirrhosis or heart issues if present. Choose ‘Absent’ if you don’t have this problem; that’s one less thing to worry about regarding your liver health! Check the box for how much fluid you see in your belly, called ascites. You can choose none, slight, or more.
- Encephalopathy Then think about your mind and nerves; this is encephalopathy. Pick if you have none, some little problems (Grades 1-2), or big problems (Grades 3-4).
- Results After that, click the “Calculate” button. Our tool quickly tells you how many points you get. It shows what Child Class you are in too.
Examples of Calculations
Let’s say a person with liver cirrhosis has the following values: Bilirubin at 2.5 mg/dL, Albumin at 3 g/dL, INR above 2.2, mild ascites, and Grade 1 encephalopathy. You punch these numbers into our calculator—pick bilirubin between 2-3 mg/dL, albumin from 2.8-3.5 g/dL, check off the highest INR option, and select slight ascites and Grade 1-2 encephalopathy.
After hitting calculate, you get a score that tells you how serious the liver damage is.
For another example, imagine someone has better results with a bilirubin level below 2 mg/dL, high albumin over 3.5 g/dL, an INR less than 1.7 without any fluid in their belly, or confused thinking due to poor liver function.
Their input in the calculator gives them a lower score which means their liver is doing better compared to other patients with more severe disease.
After finding out the score from our Child-Pugh Calculator, you can learn about what it means for treatment choices or if surgery might be needed next.
Understanding your liver’s health is key. The Child Pugh Calculator can help with that. It takes important details about your liver and uses them to figure out a score. This score tells you if your liver is doing okay if it’s facing some problems, or if it needs urgent care.
Think about how this tool could change things for you or someone else with liver issues. Ready to try our calculator? Just enter numbers for five liver health signs and click “Calculate.” You’ll get clear results that show the next steps to take for better health.
Remember, staying on top of liver health can make a big difference. Use the scores from our calculator as a guide. Talk with a doctor about what they mean for treatment options or maybe even surgery.
Our calculator offers more than just numbers; it gives hope and direction. With each bit of information, you’re taking control of your well-being—a powerful step towards healing!
FAQs
1. How does the Child Pugh score help doctors with treatment plans?
Doctors use the Child-Pugh score to decide on treatments and if a patient can handle surgeries, like trans jugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts or elective surgery.
2. Can the Child Pugh classification tell me about my risk of liver cancer?
Yes, it helps doctors figure out risks, including liver cancer stages in people with diseases like hepatitis B and C or other conditions that hurt your liver.
3. What factors are important for calculating a person’s Child Pugh score?
Important factors include bilirubin levels, creatinine level, whether there’s fluid buildup in your belly (ascites), brain function affected by your liver (hepatic encephalopathy), and how well your blood clots using INR.
4. Is the MELD Score different from the Child Pugh classification?
Yes – while both measure how serious your liver problem is, they look at different signs; MELD focuses more on kidney function and has become widely used for transplant lists.
5. Does having viral hepatitis affect my Child Pugh score?
It might – be because viruses cause scarring in the liver tissue which can lead to more symptoms affecting scores related to things like portal hypertension or varices.
Related Calculators: